physiologic tooth mobility
Pathologic tooth mobility 1. Physiological and pathological factors of tooth mobility Physiological and pathological factors of tooth mobility Physiological and pathological factors of tooth mobility Rev Belge Med Dent.
Allow physiologic tooth mobility to aid in periodontal ligament healing.

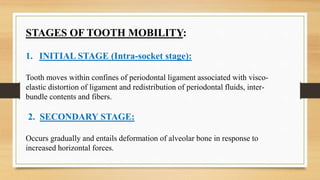
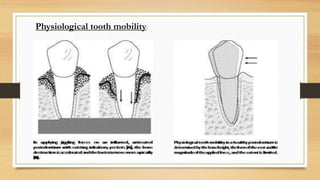
. Mobility is a measurement of horizontal. Physiological force rise time of about 50-100 ms and displacement of 10-100 μm requires high. Tooth mobility should be determined using two single-ended instruments eg mouth mirror and probe.
Normally tooth is attached to bone with periodontal ligaments so there is natural and physiologic tooth mobility of up to 025mm. 12 It is believed that hormonal fluctuations such as those. Trauma damage or injury.
August 10 2021 Post category. Grade 0 mobility Normal physiologic tooth mobility. Stabilize the injured toothteeth in its correct position and maintain adequate stabilization throughout the splinting period.
Comparing the deflection under load of dental implants with teeth provides valuable input for designing restorations spanning both teeth and implants. Tooth Mobility - Miller Classification Class 0. It refers to moderate force exerted on the crown of the tooth surrounded by a healthy and intact periodontium and tooth will show tipping movement until a closer contact has been.
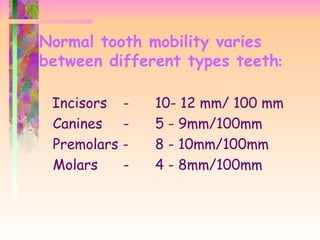
In vivo measurement of the mobility of teeth under physiological loading has been subject of research for years. Grade 1 detectable mobility up to 1mm horizontally Grade 2 detectable mobility more than 1mm horizontally Grade 3 detectable vertical tooth mobility. Occlusal movements should not be interfered.
Inability to depress the tooth in a vertical direction apicocoronal. The teeth were clinically normalThese teeth were classified into 4 groups according to their degree. Article in French Daniel A Aouizerat C Fournier B Brulin H Rassat P Praud J.
PHYSIOLOGIC TOOTH MOBILITY It refers to moderate force exerted on the crown of tooth surrounded by a healthy intact periodontium tooth will show tipping movement until a closer contact has been established between root marginal bony tissue. Article in French Authors L Gharbi-Guesguez 1 D Abassi-Bakir A Bakir. PHYSIOLOGICAL TOOTH MOBILITY.
Physiologic dental mobility. Allow adequate oral hygiene. It should be nonirritating to soft tissues.
Comparing the deflection under load of dental implants with teeth provides valuable input for designing restorations spanning both teeth and implants. In vivo measurement of the mobility of teeth under physiological loading has been subject of research for years. The subjects in this study were 129 maxillary primary central incisors and 201 maxillary primary lateral incisors of patients between 2 years and 11 months-old and 9 years and 4 months-old.
It refers to a moderate force exerted on the crown of tooth surrounded by a healthy intact periodontium tooth will show tipping movement until a closer contact has been established between root marginal bony tissue. 1077339 PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE MeSH Terms Dental Stress Analysis Facial Musclesphysiology Humans Mastication Periodontiumphysiology Toothphysiology Tooth Mobility. Not interfere with occlusal movements.
Tooth can be moved up to 1mm or more in a lateral direction buccolingual or mesiodistal. A retrospective study noted that dental mobility may be the inaugural sign of osteolytic processes in the maxillar. In both cases the name for the condition of tooth looseness is occlusal trauma occlusal bite.
Grading of tooth mobility greatly defines the success of procedure. It should allow pulp sensibility testing and endodontic access. Not irritate soft tissues.
Physiologic mobility represents the range of mobility level considered normal. Tooth mobility should be determined using two single-ended instruments and assessed according to the criteria. Physiologic tooth mobility.
This can in effect stretch the periodontal ligaments which join the teeth to the supporting bone with the result that the teeth become loose. This video is about How to assess TOOTH MOBILITYPdf notes available. Maintenance of adequate oral hygiene should be possible.
MOBILITY CAN BE OF TWO TYPES. TOOTH MOBILITY can be defined as the degree of looseness of a tooth KENRY AAP 1986 Mobility is recorded as a part of the initial occlusal evaluation to monitor changes overtime In health physiological or functional mobility of tooth exists every tooth with healthy periodontal support will have a physiologic range of mobility. Allow pulp sensibility testing and endodontic access.
Physiologic mobility refers to the slight degree of movement that all teeth even perfectly healthy ones have when some force is applied. Therefore determining tooth mobility gives useful information for the diagnosis and evaluation of the treatment outcome. Dental mobility can in fact be the first sign of osteolytic processes or tumour development.
It is useful because it helps both to define and treat it. Download link is as follows. Normal physiologic movement when force is applied.
There are three grades of tooth mobility. It should fulfill esthetic appearance and should be comfortable for the patient. It should allow physiologic tooth mobility.
This study was conducted in order to estimate the physiological tooth mobility in primary teeth. Fixed reference point should be selected eg adjacent tooth that is not mobile and pressure should be applied in horizontal buccal-oral direction to the tooth we are testing. Tooth mobility disclosing an osteolytic process Rev Stomatol Chir Maxillofac.
Mobility beyond the physiologic range is termed. Article in Dutch Author D vanSteenberghe. In vivo measurement of the mobility of teeth under physiological loading has been subject of research for years.
Physiological tooth mobility seen in healthy teeth depends on the biophysical characteristics of the periodontal tissue whereas pathological tooth mobility is the result of the loss of periodontal support. Mobility greater than physiologic. Grade 1 is 1-2 mm tooth mobility.
Comparing the deflection under load of dental implants with teeth provides valuable. Grade 0 Normal physiologic tooth mobility. This can be reversed by professional scaling polishing and maintenance for at least 1 month at.
PHYSIOLOGIC PATHOLOGIC TOOTH MOBILITY TOOTH MOBILITY 4.

8 Signs Symptoms Of Gum Disease By Dr Somit Jain Gum Disease Swollen Gum Gingival Recession
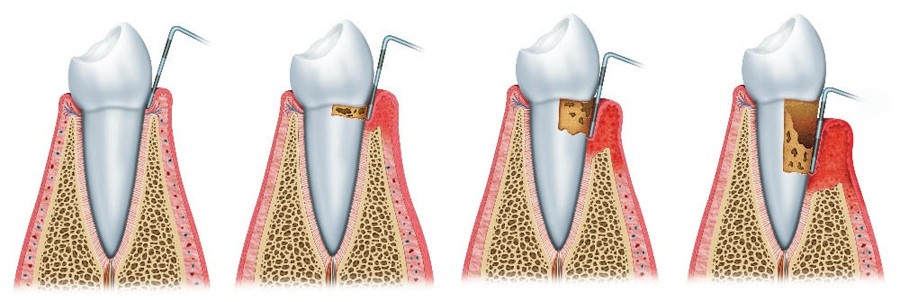
Tooth Mobility And Periodontal Therapy My Dentist Toluca Lake

Orthodontic Tooth Movement The Biology And Clinical Implications Li 2018 The Kaohsiung Journal Of Medical Sciences Wiley Online Library

Cmtautodom Gif 397 435 Pixels Teeth Diseases Neurology Cmt

Carnivore Omnivore Herbivore Frugivore Human Spot The Differences Https Www Facebook Com Photo Php Fbid 7511411 Omnivore Carnivores Carnivore Teeth

Effects Of Periodontitis Associated Tooth Mobility With Positive Feedback Download Scientific Diagram
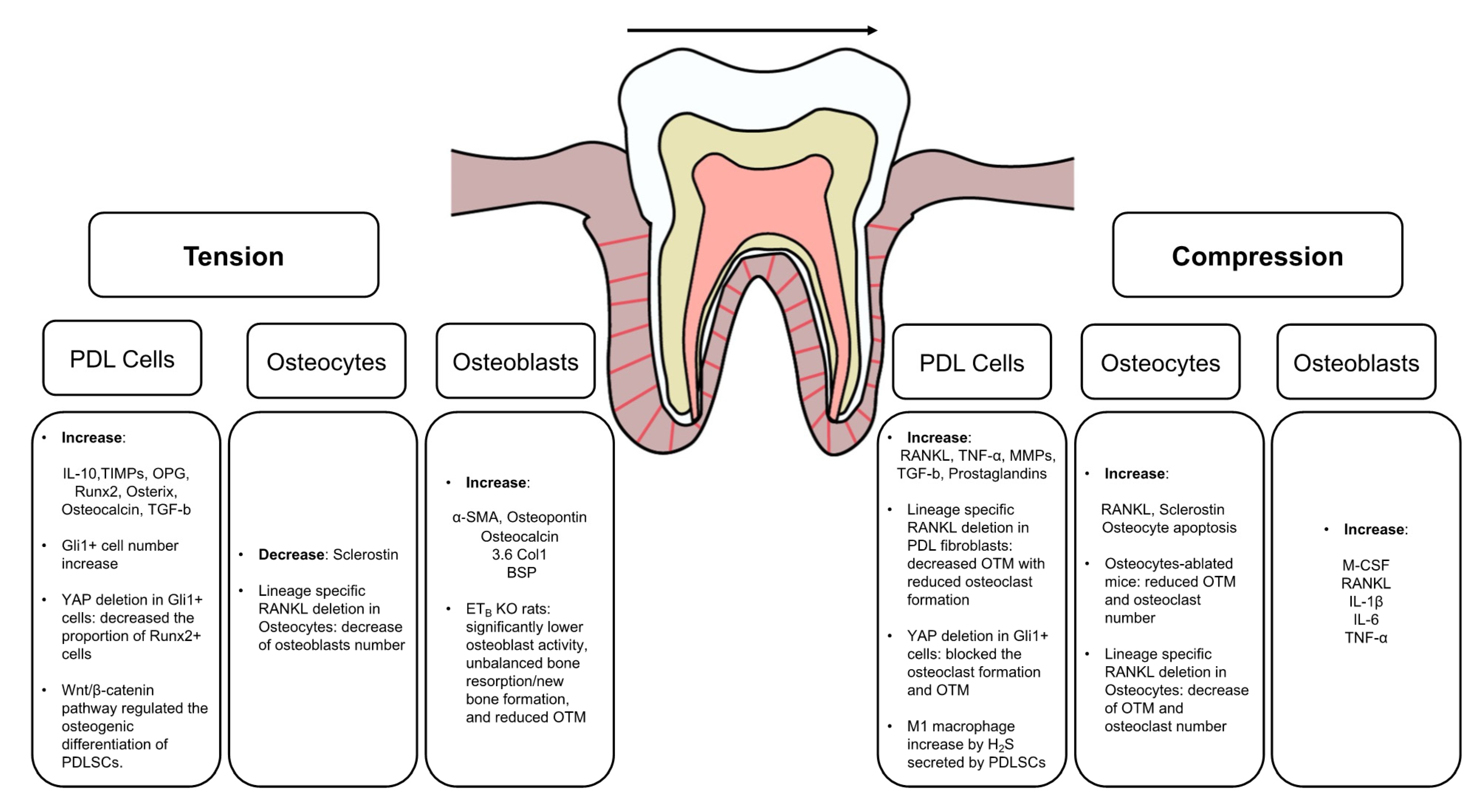
Jcm Free Full Text Mechanistic Insight Into Orthodontic Tooth Movement Based On Animal Studies A Critical Review Html

Image From Http Www Mhhe Com Biosci Esp 2001 Saladin Folder Structure Su M3 S1 Assets Images Sum3s1 1 Jp Joints Anatomy Synovial Joint Anatomy And Physiology

Body Cavities And Membranes Medical School Studying Nursing School Medical Anatomy

Pin By Jennifer York On Cmt Charcot Marie Tooth Teeth Diseases Point Mutation Cmt

Physiotherapy Kinesiology What S The Difference Infographic Physiotherapy Kinesiology Education Resour Kinesiology Anatomy And Physiology Physiotherapy

Figure 284a B Medical Massage Medical Anatomy Dental Assistant





Comments
Post a Comment